What do SIBECOL ecologists do?
The field of Ecology studies the relationships between living organisms and their environment. By gathering information on ecosystems, Ecology helps us to understand how the world works as well as to identify the the major threats it faces. Among other things, the application of Ecology implies habitat restoration, biodiversity protection, and natural resources management.
The ecologists of the Iberian Peninsula study all kinds of ecosystems and organisms. In this section, SIBECOL researchers share their latest studies in Ecology.
Ready to know their research?
You are a SIBECOL member and want to share a review article or important article? Write us at clararg@icm.csic es or fpicazo@ugr.es
*The editorial team will assess the suitability of the content for this section

Urea as an overlooked source of nitrogen and energy for deep-sea microorganisms
The microbial ecologist Nestor Arandia-Gorostidi and collaborators demonstrate that urea is a previously overlooked but widespread nitrogen and energy source for deep-sea microorganisms, fueling microbial food webs in the dark depths of the ocean. [read more]

When Rivers Dry Up: How Aquatic Bacteria Adapt to Terrestrial Life
Microbial ecologist Anna Freixa and collaborators investigate how river bacterial communities survive when rivers dry up, revealing the emergence of 'terrestrial' bacteria in sediments of temporary rivers [read more].
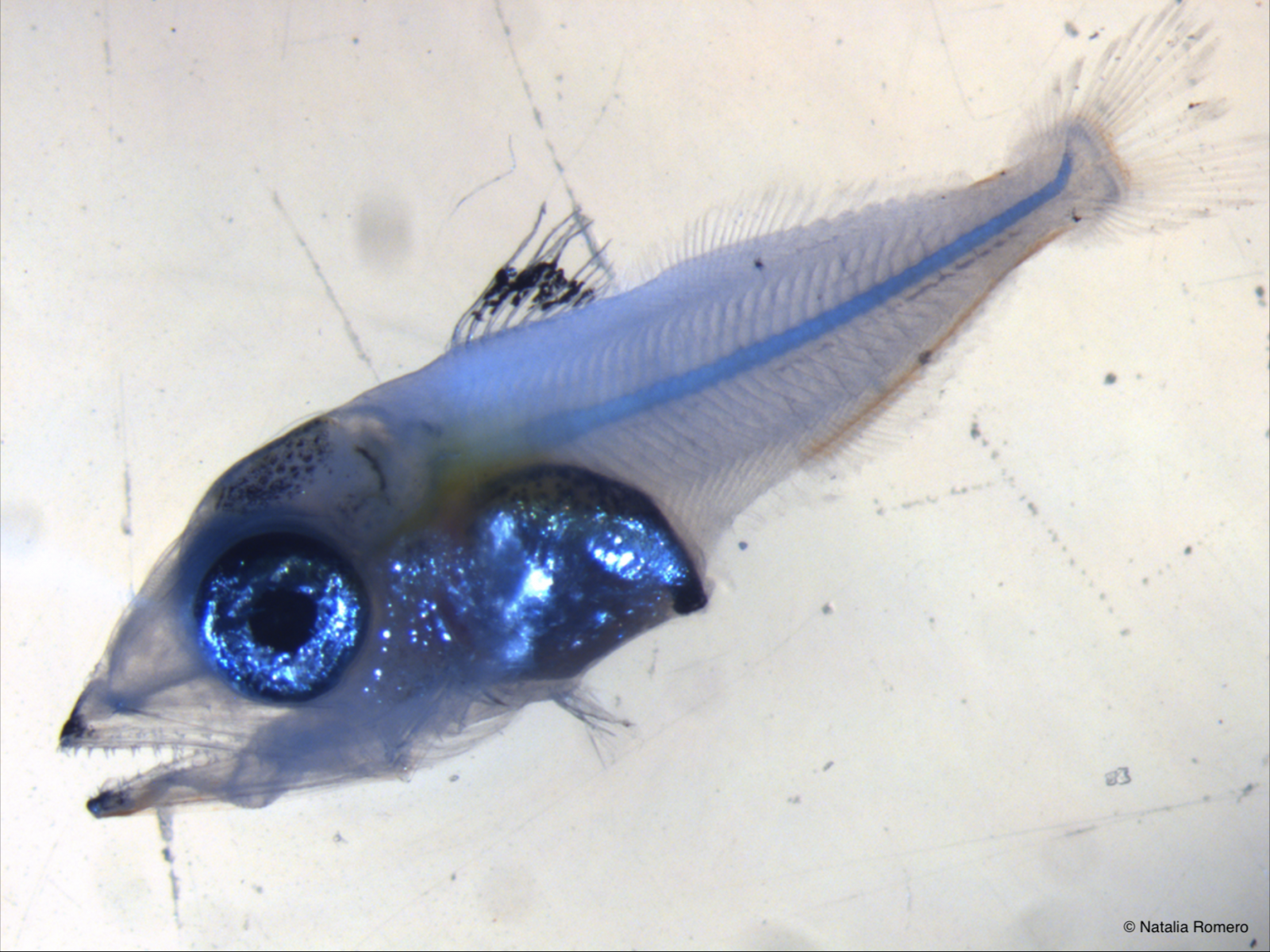
The maternal inheritance, key to the survival of bluefin tuna Larvae
The marine ecologist Ricardo Borrego-Santos and his collaborators study the survival of bluefin tuna larvae, a specie of great commercial value, demonstrating the crucial role of maternal inheritance, as well as the importance of the environment and food availability for their development. [read more]
.JPG)
A seed dispersal crisis threatens European vegetation
The ecologist Sara Beatriz Mendes and collaborators reveal the poor conservation state of many animal dispersers of plant seeds in Europe, which threatens the survival of vegetation across most European biomes. [read more]

Searching for methylmercury degrading microbes in the deep ocean
The microbial ecologist Isabel Sanz-Sáez and her collaborators explore the presence and distribution of mercury degrading microbes in the deep ocean, revealing a wide distribution of microbes carrying the genes involved in this process. [read more]%20Andrena%20pilipes%20%E2%99%80%EF%B8%8E%20en%20Cistus%20albidus(1).jpeg)
Tell me who you interact with, and I will tell you if you survive
The ecologists Virginia Domínguez-García, Ignasi Bartomeus, and collaborators have developed a model that allows to predict the characteristics of plant and pollinator populations that confer greater resistance to environmental changes. [Read more]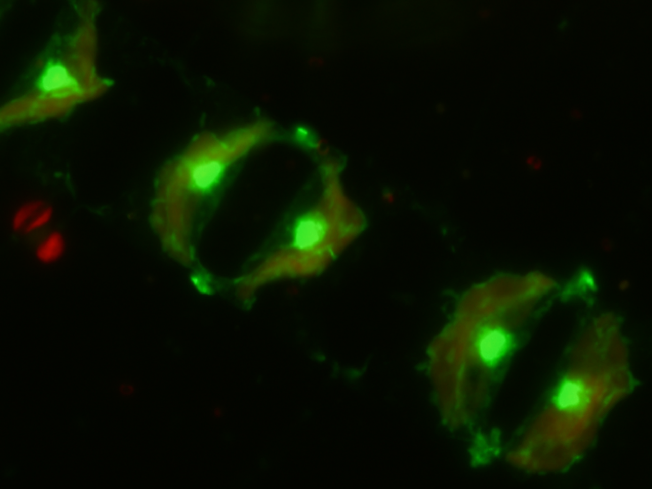
Exploring the use of organic substrates by marine phytoplankton through microscopy
The microbial ecologist Catalina Mena and her collaborators explore the incorporation of organic matter by marine microalgae, a well-known but poorly quantified process, revealing a large diversity of species able to incorporate organic substrates that potentially compete with bacteria. [read more] The microbial ecologist Elizabeth León-Palmero and her collaborators study the production of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, in several reservoirs, showing that its production or consumption depends not only on the availability of nitrogen and oxygen, but also of phosphorus, and of how these elements regulate denitrifying bacteria [read more]
The microbial ecologist Elizabeth León-Palmero and her collaborators study the production of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, in several reservoirs, showing that its production or consumption depends not only on the availability of nitrogen and oxygen, but also of phosphorus, and of how these elements regulate denitrifying bacteria [read more]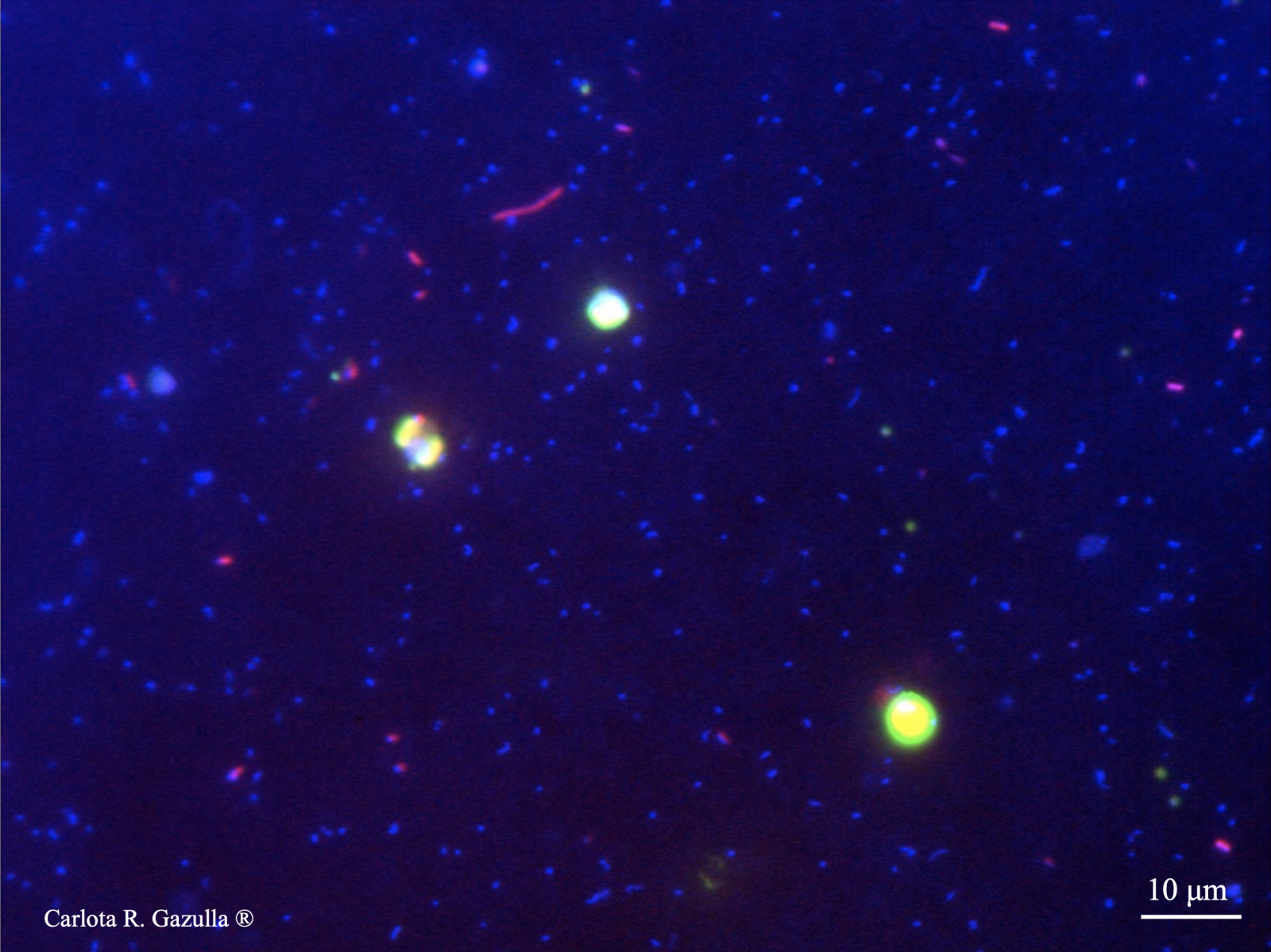
Optimizing the genetic tools study a relevant group of marine bacteria capable of using solar energy
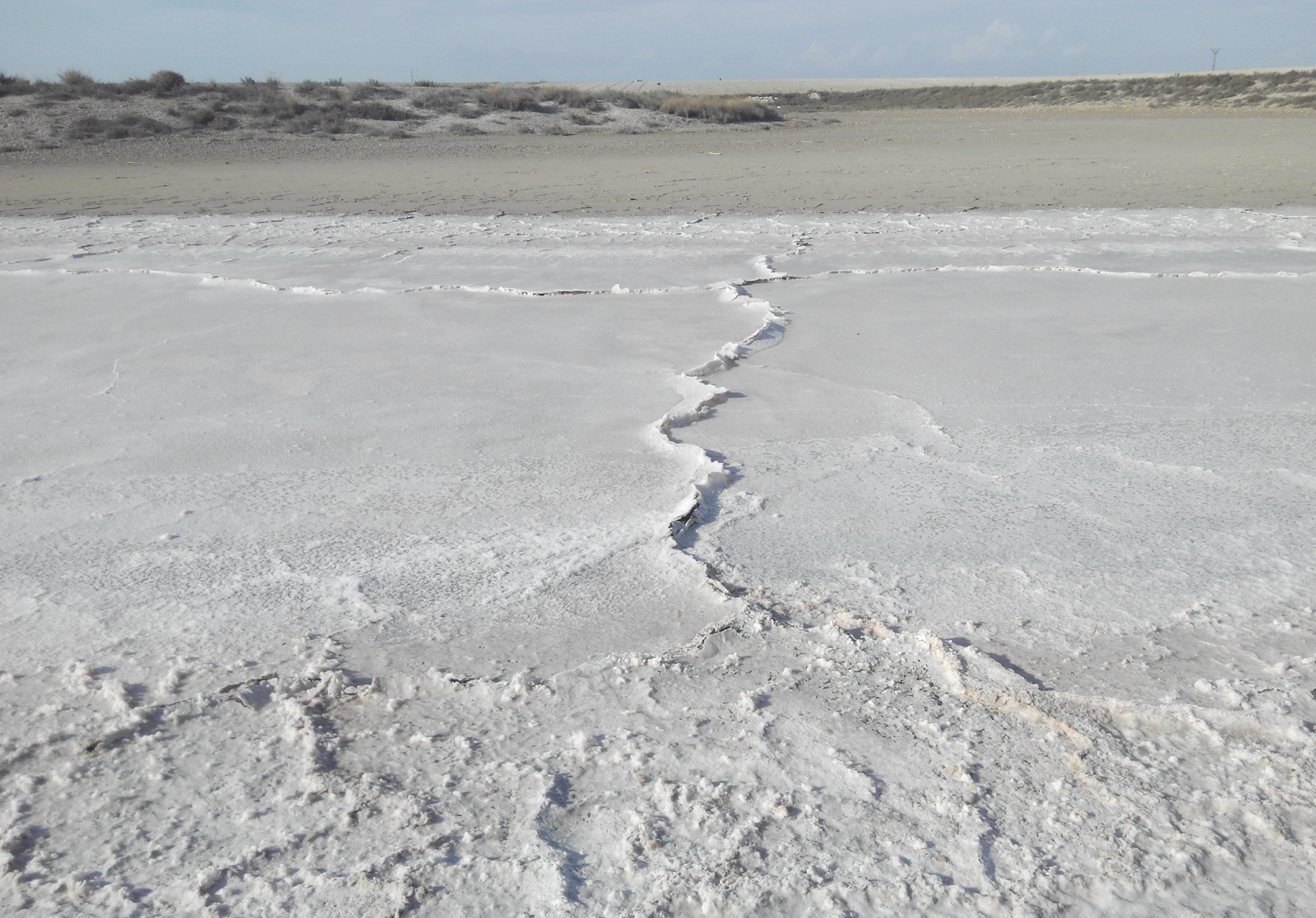

Freshwater salinisation: a research agenda for a saltier world
.jpeg)
Counting bacteria in the ocean faster than ever: automated flow cytometry
The microbial ecologists Massimo Pernice and Josep M. Gasol present an automated system to count marine bacteria during oceanographic cruises, improving the spatial and temporal resolution of bacterial numbers in the ocean [read more]
Deep ocean prokaryotes are healthier under highly productive surface waters
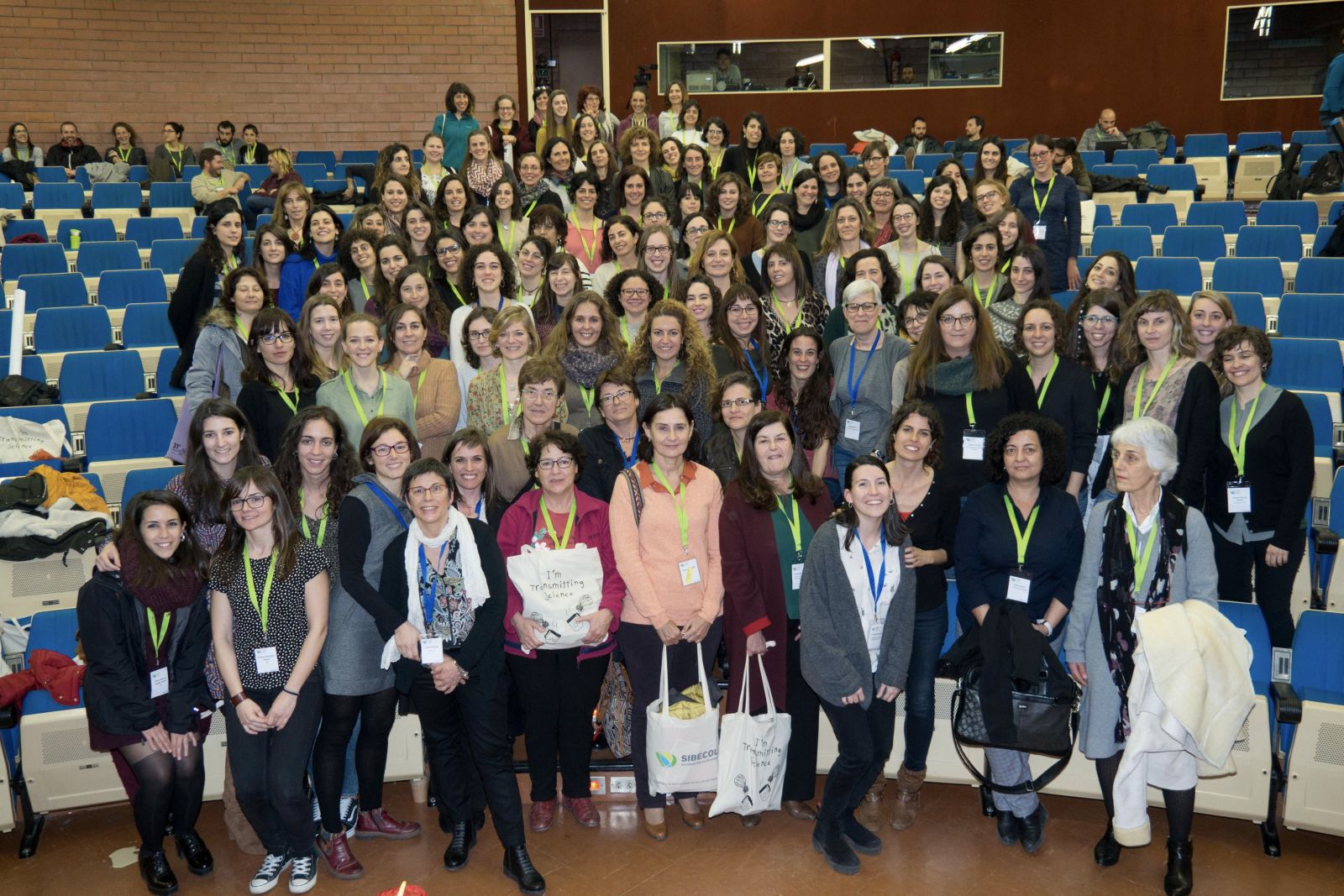

Evaluating the gender equity in the first SIBECOL meeting
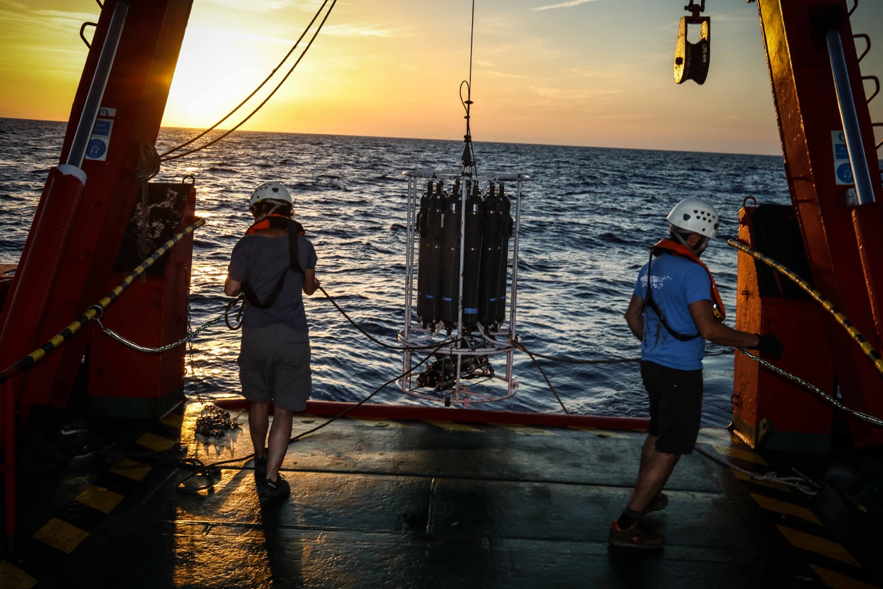

Tracking the diversity of Mediterranean Sea microbes from East to West
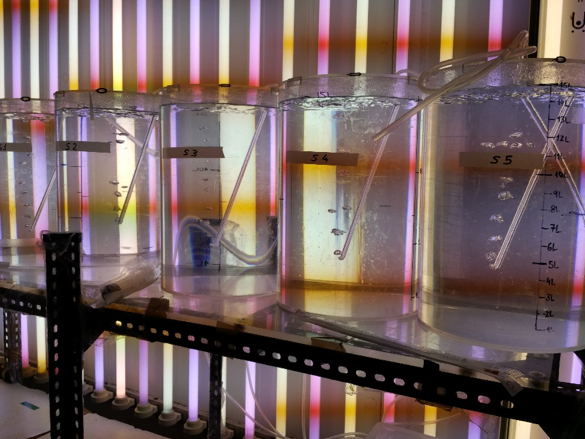

Diatoms, hard-to-degrade marine microalgae, are efficient at removing atmospheric CO2
.png)
The need to include functional indicators in stream and river bioassessment
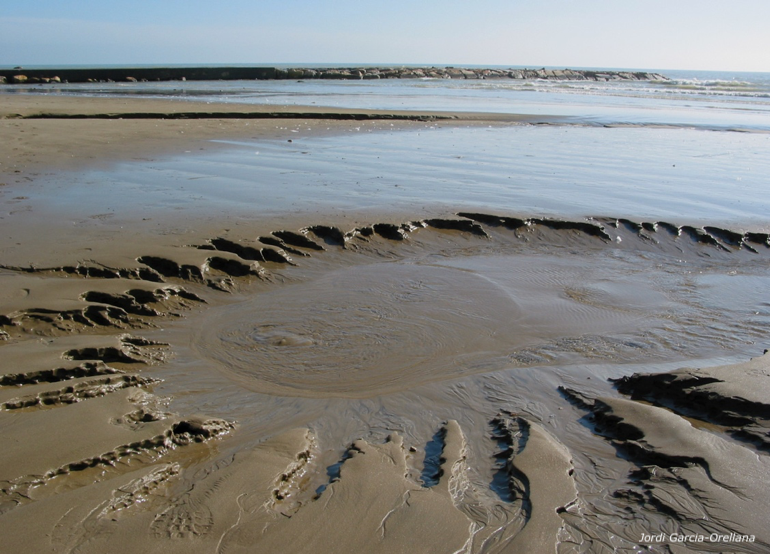

The microbial dimension of submarine groundwater discharge

Predicting the effects of forest invasion by nitrogen-fixing trees on streams
The limnologist Verónica Ferreira and collaborators address the effects of the invasion of deciduous riparian forests by exotic nitrogen-fixing species and identify three main pathways by which they can affect stream communities and processes. [read more]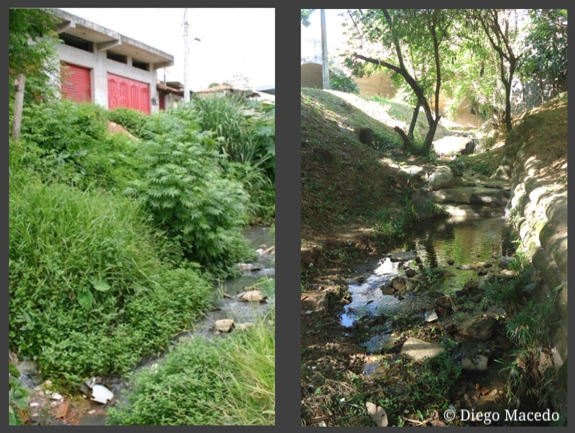
Poor health and reduced implementation of rehabilitation programs in many rivers around the globe
The limnologist Maria João Feio and collaborators reviewed the existing river bioassessment and rehabilitation programs in the world and identify actions that should be taken for the protection and recovery of these systems. [read more]
The maternal inheritance, key to the survival of bluefin tuna Larvae
The marine ecologist Ricardo Borrego-Santos and his collaborators study the survival of bluefin tuna larvae, a specie of great commercial value, demonstrating the crucial role of maternal inheritance, as well as the importance of the environment and food availability for their development. [read more]

When Rivers Dry Up: How Aquatic Bacteria Adapt to Terrestrial Life
Microbial ecologist Anna Freixa and collaborators investigate how river bacterial communities survive when rivers dry up, revealing the emergence of 'terrestrial' bacteria in sediments of temporary rivers [read more].
