Exploring the use of organic substrates by marine phytoplankton through microscopy
By Catalina Mena and collaborators
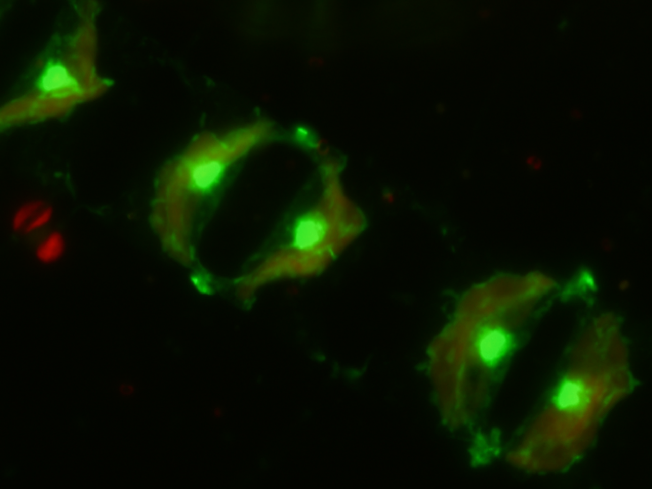 In the ocean, the main primary producers are the phytoplankton, microscopic algae that use the energy of light to produce organic carbon through photosynthesis. Some of this carbon is released to the environment as dissolved organic matter, which is considered to be mainly consumed and transformed by heterotrophic bacteria. However, most phytoplankton are also capable of complementing their photosynthetic capacity by absorbing dissolved organic compounds from the environment, but the relevance of this process in the marine carbon cycle is still unclear. In this work, we explored the capacity of phytoplankton communities from the NW Mediterranean to incorporate an organic compound (an amino acid) during 9 days. We used a technique called BONCAT that allows to fluorescently label the cells that have incorporated the organic substrate and visualize them through microscopy. We found a large diversity of phytoplankton groups capable of using the organic substrate and, moreover, some of the groups showed daily changes in its incorporation. Among them, large groups such as diatoms were responsible for up to 86% of the substrate incorporated by phytoplankton and other eukaryotic organisms. Finally, when bacteria were also considered, we estimated that eukaryotes accounted for 19-31% of the total substrate incorporation. Our results indicate a large complexity in the phytoplankton incorporation of organic substrates, which varied depending on the species present and even over time within phytoplankton groups. Overall, the findings highlight the potential of the BONCAT technique to quantify phytoplankton uptake of organic matter in complex marine microbial communities, and call for the need to better understand the role that this process might have in the ocean carbon fluxes.
In the ocean, the main primary producers are the phytoplankton, microscopic algae that use the energy of light to produce organic carbon through photosynthesis. Some of this carbon is released to the environment as dissolved organic matter, which is considered to be mainly consumed and transformed by heterotrophic bacteria. However, most phytoplankton are also capable of complementing their photosynthetic capacity by absorbing dissolved organic compounds from the environment, but the relevance of this process in the marine carbon cycle is still unclear. In this work, we explored the capacity of phytoplankton communities from the NW Mediterranean to incorporate an organic compound (an amino acid) during 9 days. We used a technique called BONCAT that allows to fluorescently label the cells that have incorporated the organic substrate and visualize them through microscopy. We found a large diversity of phytoplankton groups capable of using the organic substrate and, moreover, some of the groups showed daily changes in its incorporation. Among them, large groups such as diatoms were responsible for up to 86% of the substrate incorporated by phytoplankton and other eukaryotic organisms. Finally, when bacteria were also considered, we estimated that eukaryotes accounted for 19-31% of the total substrate incorporation. Our results indicate a large complexity in the phytoplankton incorporation of organic substrates, which varied depending on the species present and even over time within phytoplankton groups. Overall, the findings highlight the potential of the BONCAT technique to quantify phytoplankton uptake of organic matter in complex marine microbial communities, and call for the need to better understand the role that this process might have in the ocean carbon fluxes.Read the full study here:
Mena C, Deulofeu-Capo O, Forn I, Dordal-Soriano J, Mantilla-Arias YA, Samos IP, Sebastián M, Cardelús, Massana R, Romera-Castillo C, Mallenco-Fornies R, Gasol JM, Ruiz-González C (2024) High amino acid osmotrophic incorporation by marine eukaryotic phytoplankton revealed by click-chemistry. ISME Communications.
Text written by Catalina Mena and edited by Clara Ruiz and Félix Picazo
